RoboDK examples
The following examples show some basic usage of RoboDK for Simulation and Offline Programming. These examples are available with the default download.
Select File-Open in RoboDK to load a specific example.
Pick and place
Robot pick and place automation speeds up the process of picking parts from one location and placing them in another location, increasing production rates.
This video tutorial shows an overview of RoboDK for simulation and offline programming.
Robot machining
Robotic milling is becoming more and more popular in the CNC industry. RoboDK software is the perfect solution to convert NC-code to robot programs.
Easily generate robot programs free of singularities, axis limits and avoiding collisions with RoboDK.
Get started with Robot Machining
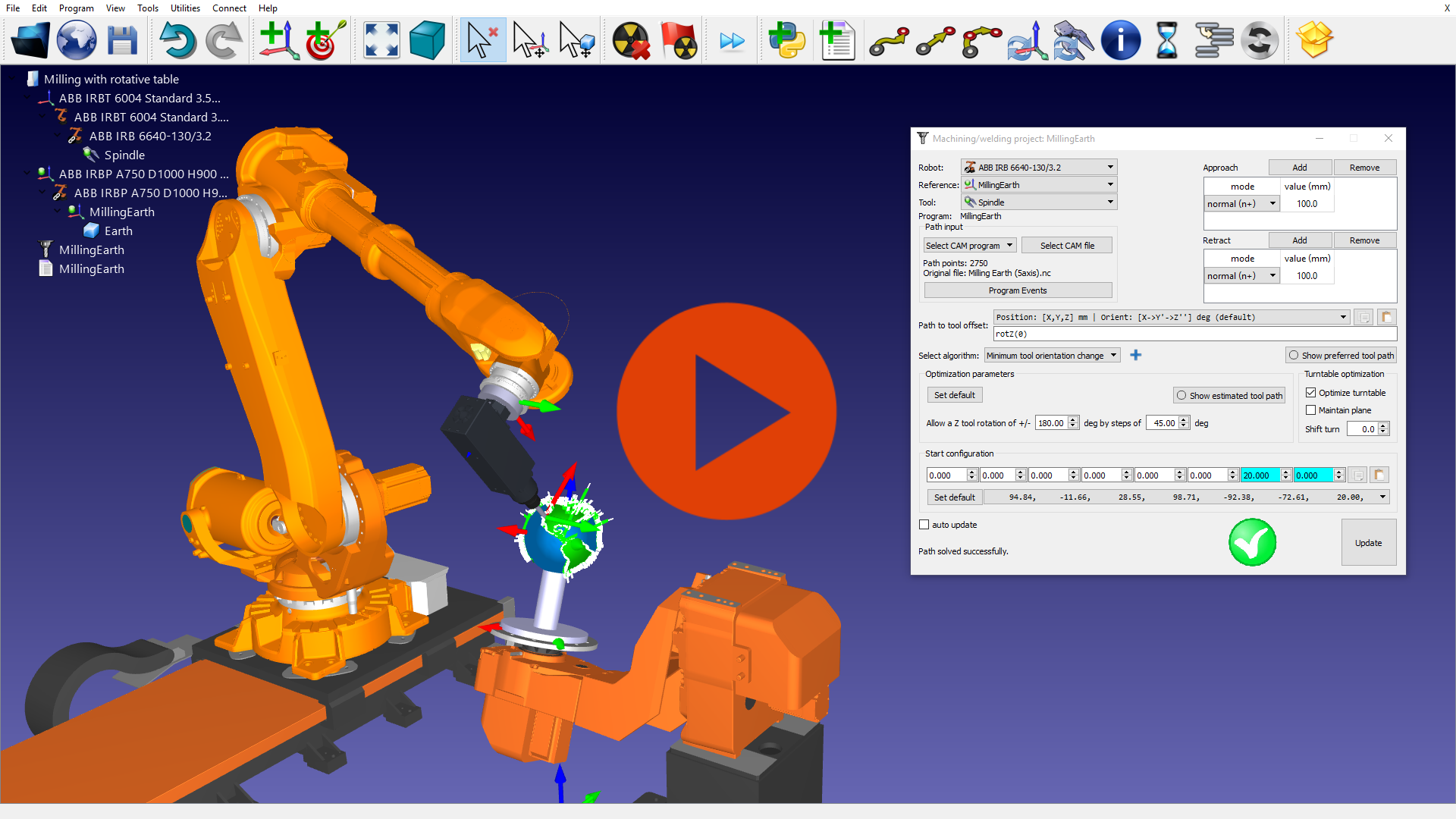
Robot Machining with external axes
External axes can be modelled and synchronized with a robot arm for robot Machining purposes. RoboDK optimizes the robot axes to generate optimal and error-free robot programs.
This example shows how an ABB robot arm can be used with a turntable to machine a spherical object.
View Robot Machining Simulation
Get started with Robot Machining
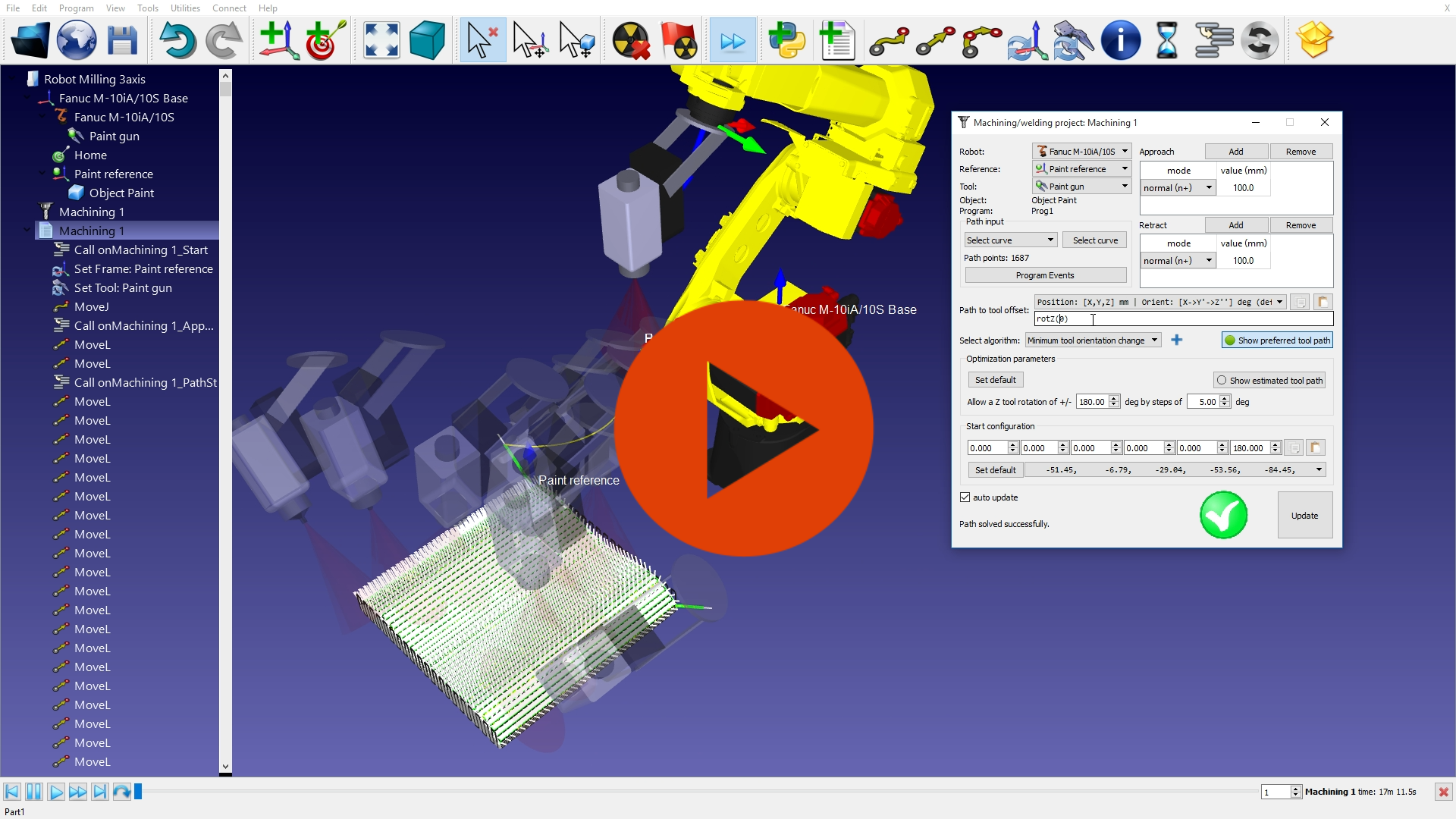
Robot Painting
RoboDK can easily generate robot paths along surfaces for painting or inspection applications. RoboDK automatically avoids robot singularities, axis limits and collisions.
Targets on a surface can also be created in a few steps and robot programs can be obtained in a matter of minutes.
View Robot Painting Simulation
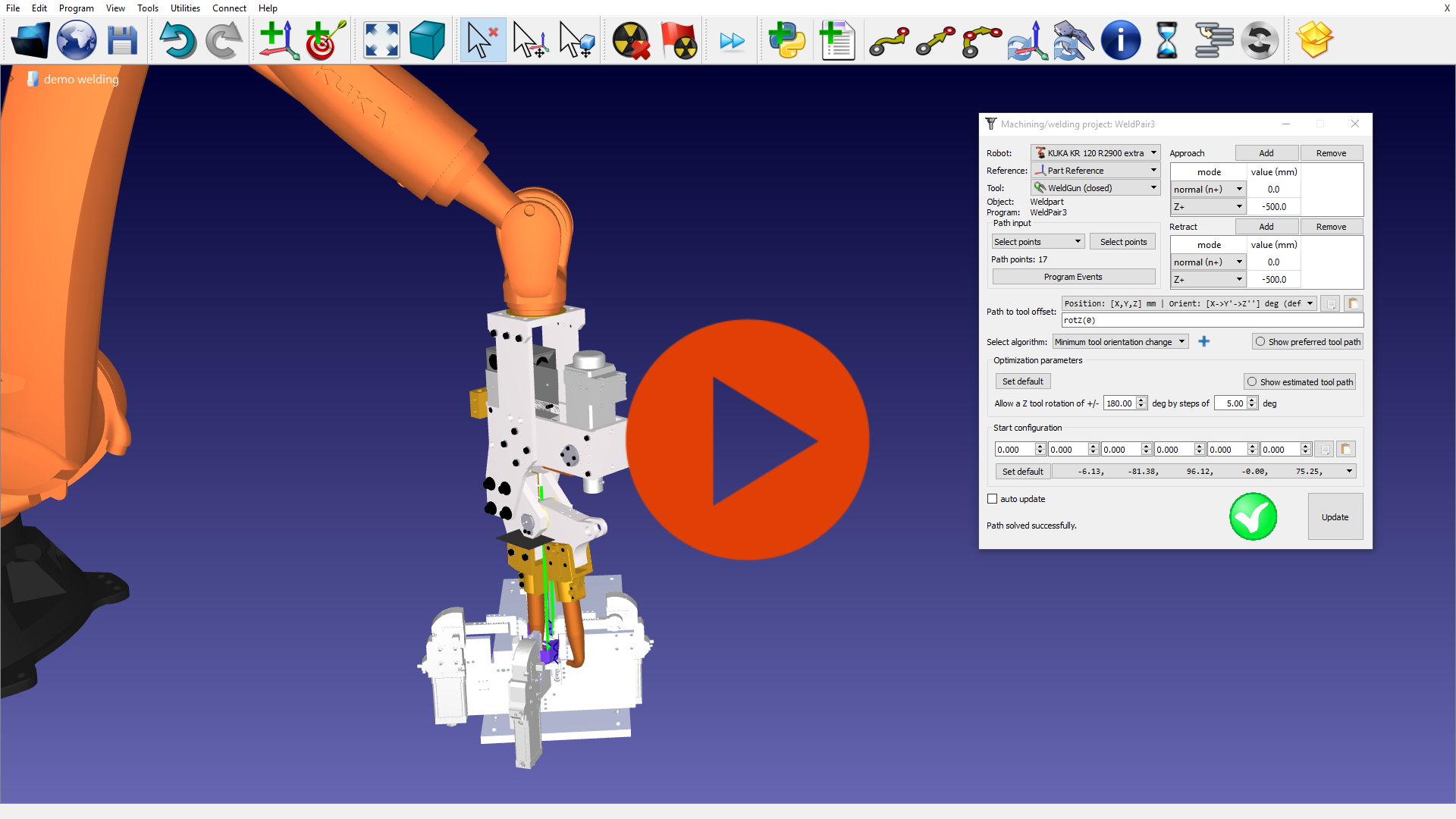
Robot Spot Welding
Robotic Spot Welding is a type of resistance welding. Spot Welding is the most common type of robot welding. RoboDK Software can easily generate error-free robot programs for spot welding applications.
This video shows a spot welding application using a KUKA robot and an HMD Technology weld gun.
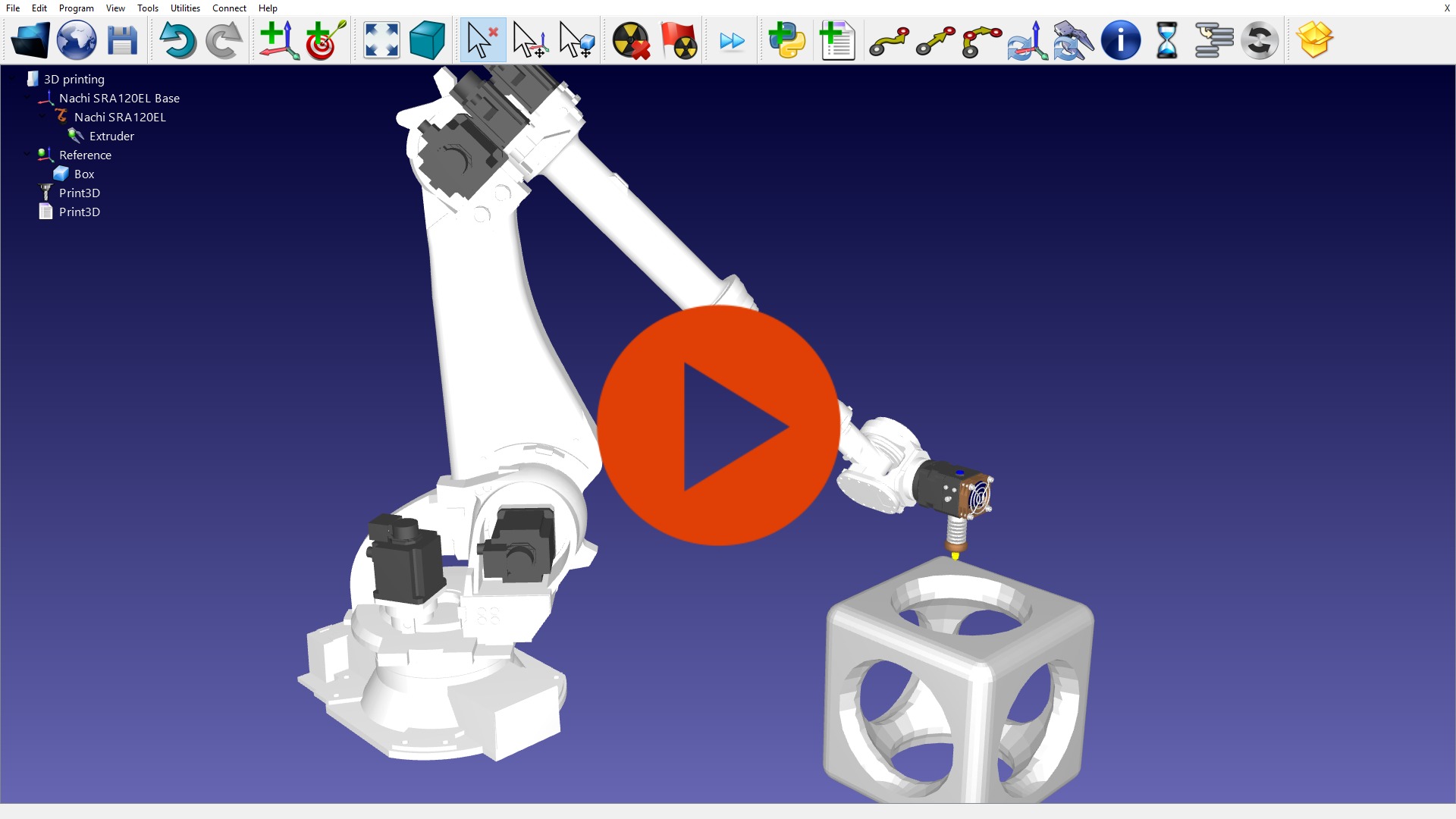
3D Printing with a robot
3D printing with robots (or additive manufacturing) allows making large three dimensional objects from a digital object file. Industrial robot arms can be used as a 3-axis or 5-axis printer with RoboDK Software to 3D print large objects. RoboDK will generate error-free robot programs.
This video shows how a Nachi robot is used to 3D print a large object.
Conveyor belt
A belt conveyor system is one of many types of mechanisms supported by RoboDK. New mechanisms such as conveyor belts, linear tracks and turntables can be modelled in RoboDK.
This example shows how two robots work together feeding and taking parts from a conveyor belt.
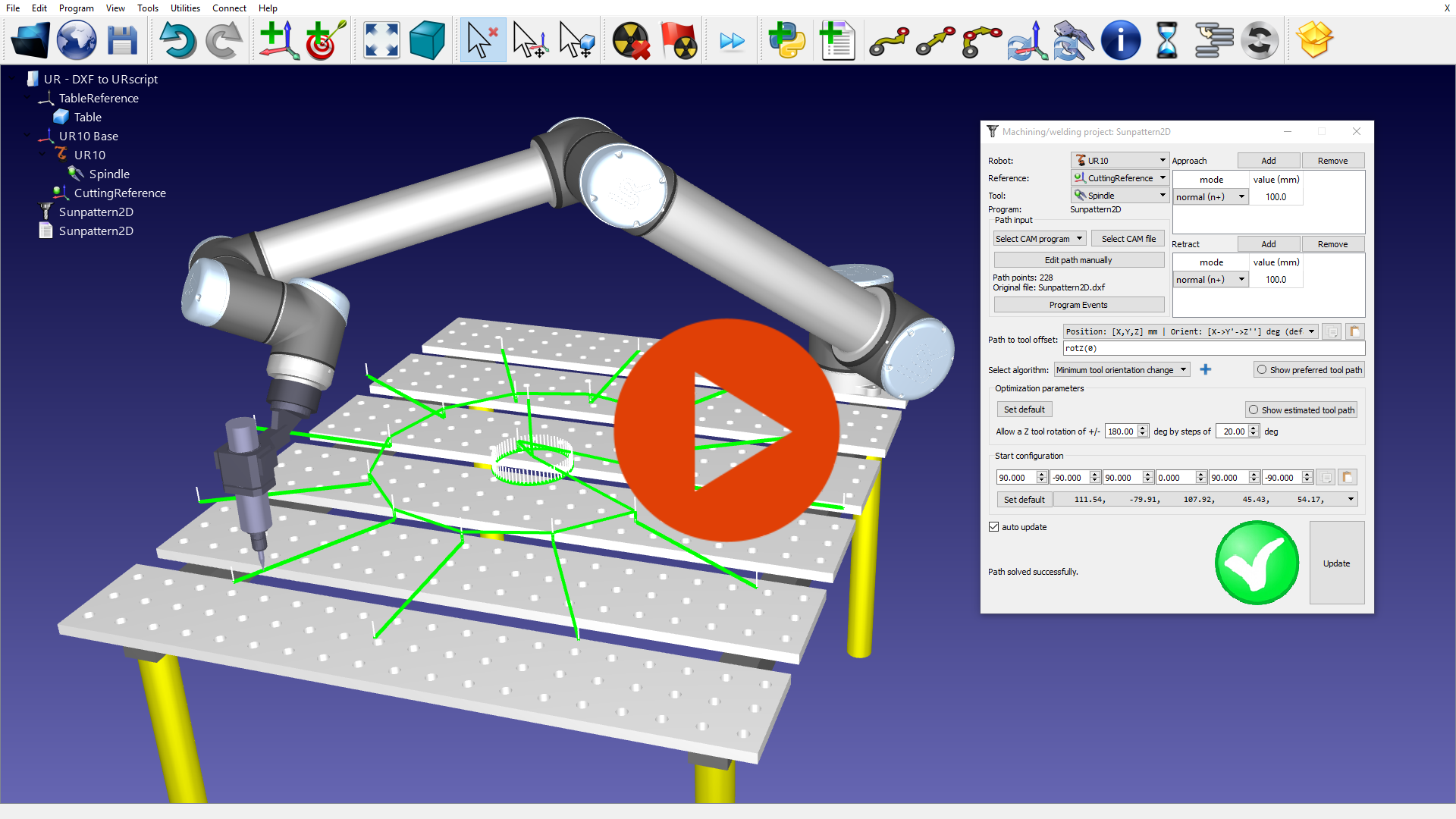
DXF to robot program
Robot programs can be generated from a DXF file using RoboDK's simulation and offline programming features.
DXF programs can be easily converted to NC-code for cutting for example. This example shows how to convert a DXF file to generate a robot program for a UR robot (SCRIPT or URP).
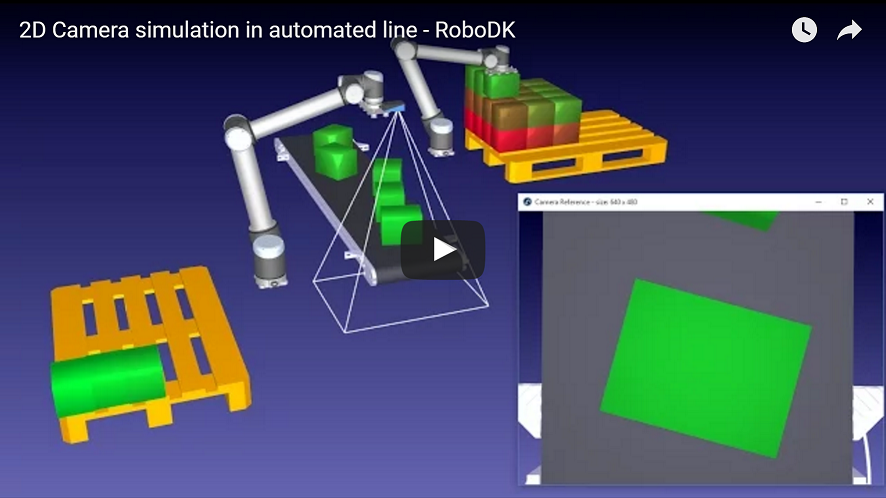
Automated Inspection
Automated inspection, also known as machine vision, is now one of the key technology areas in robotic pick and place applications. With RoboDK Software it is very easy to simulate inspection cameras and trigger simulated snapshots. All camera settings can be easily adjusted, such as the focal distance, field of view, working distance or sensor size. The workspace of the camera can also be displayed.
In this example, two robots (Universal Robots) and a 2D inspection camera perform a palletizing task.
Pick and place with Python
This example shows an advanced pick and place simulation. Moving the robot and replacing the objects is accomplished through Python.
The RoboDK's Python API allows programming any robot through Python. Additionally, you can interact with the simulator to create, modify or edit any objects or robots programmatically.
Advanced pick and place simulation
Get started with the RoboDK API
Drawing Robot
A drawing robot can automatically draw an image like an artist.
Automated drawing can be achieved using the RoboDK API. Using the RoboDK API, a 3rd party Python library can be used to convert the SVG images to robot paths.
Learn more about a real project
Get started with the RoboDK API