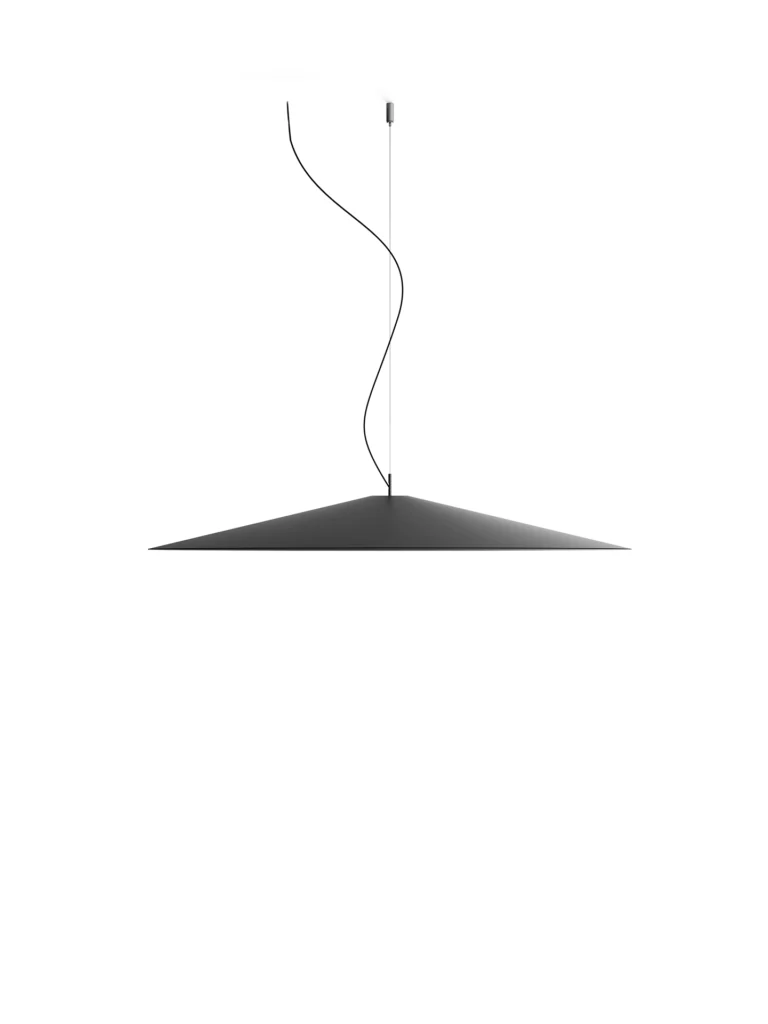
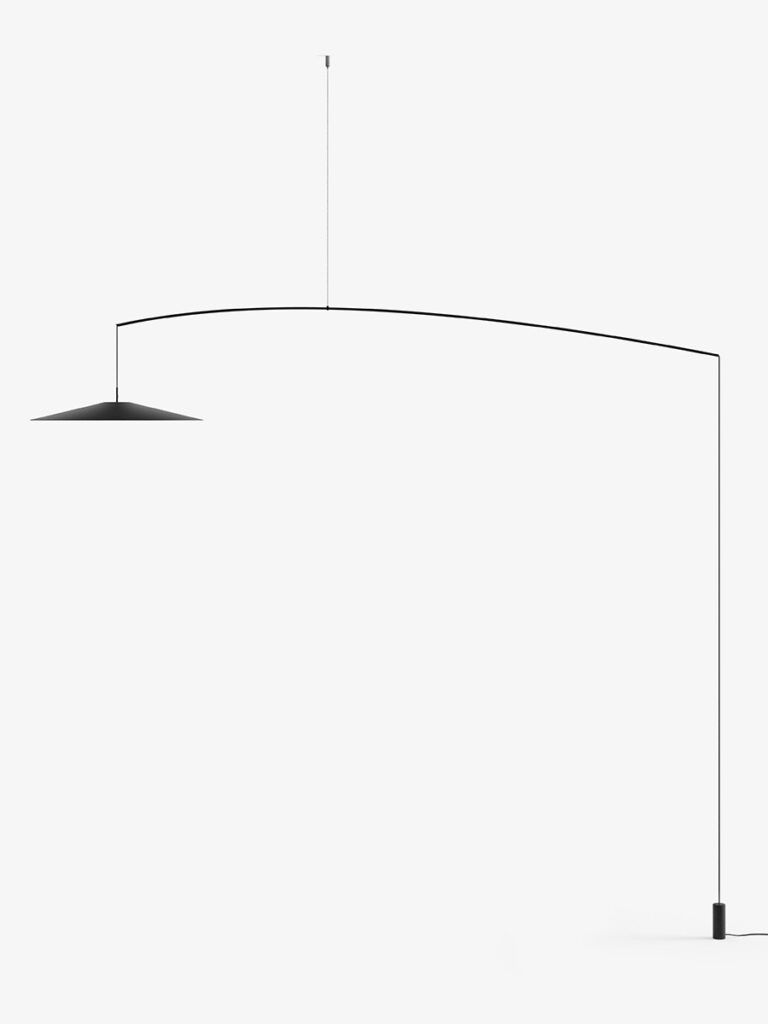
KoinèSuspension
designed by Mandalaki Studio
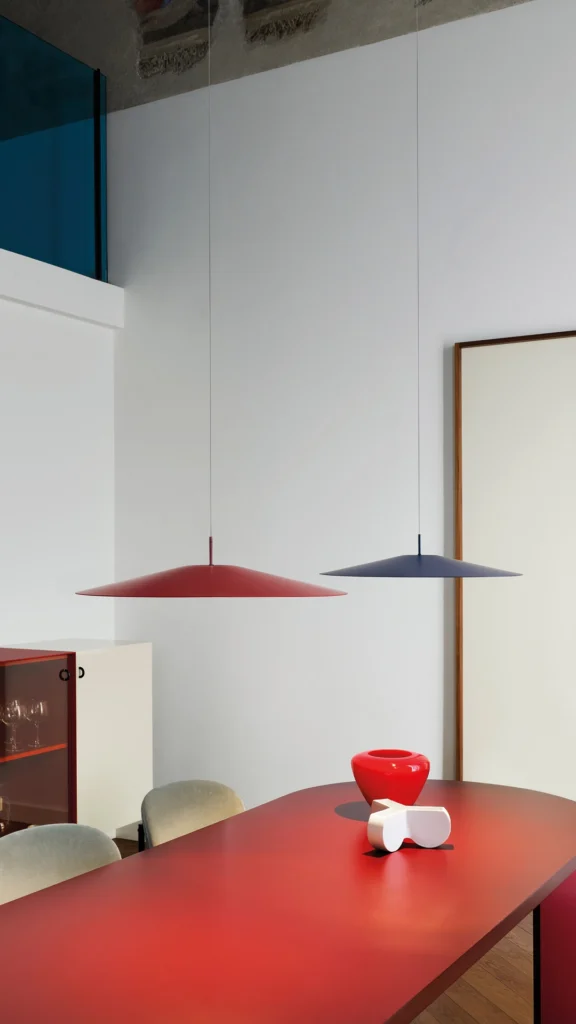
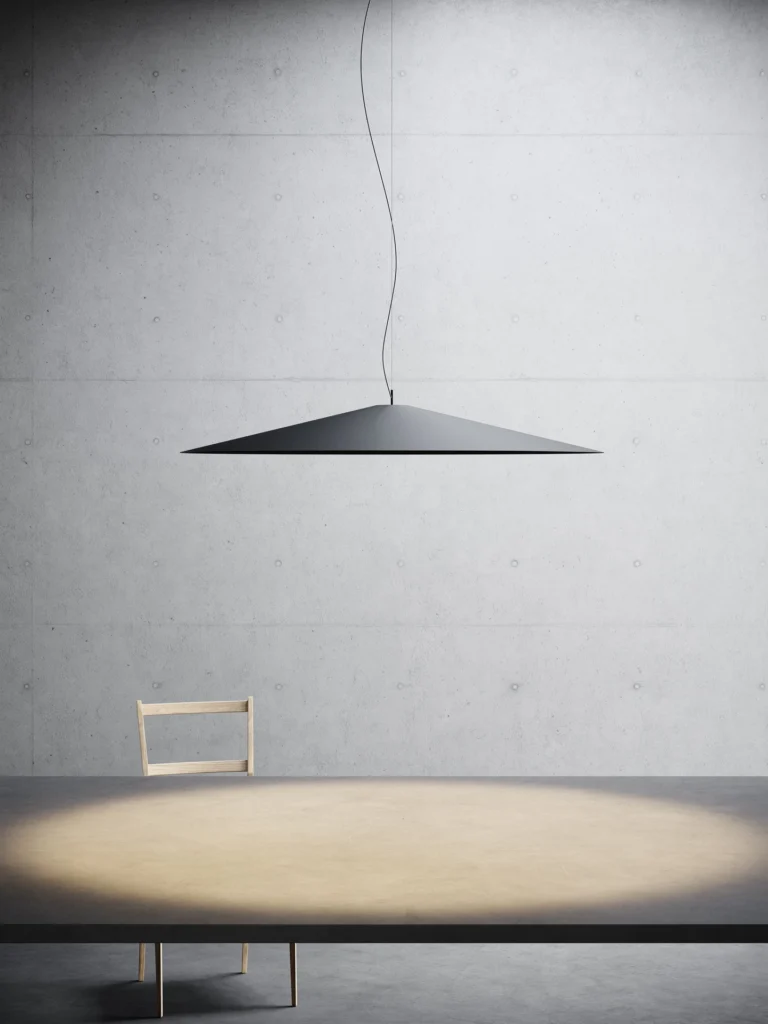
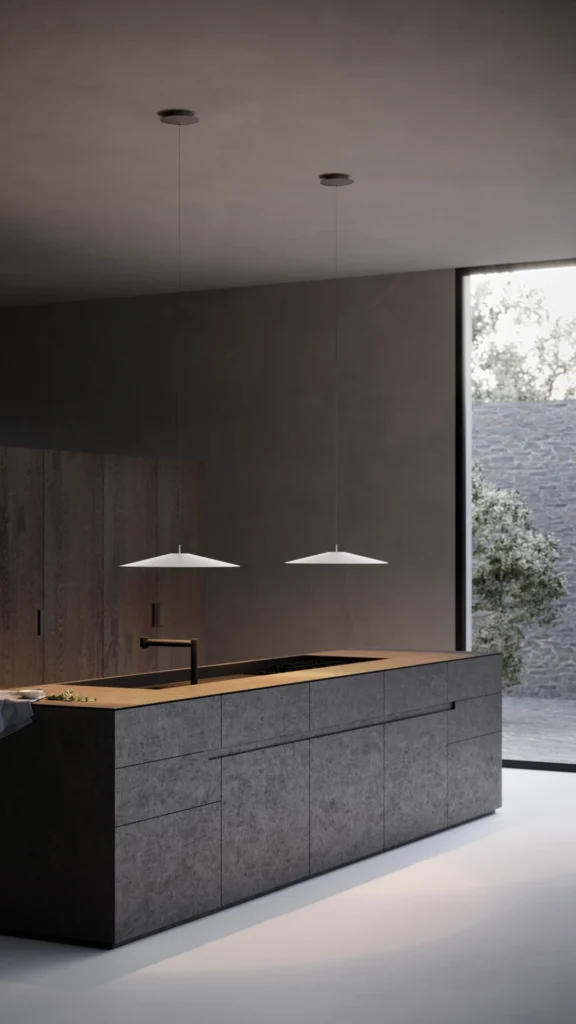
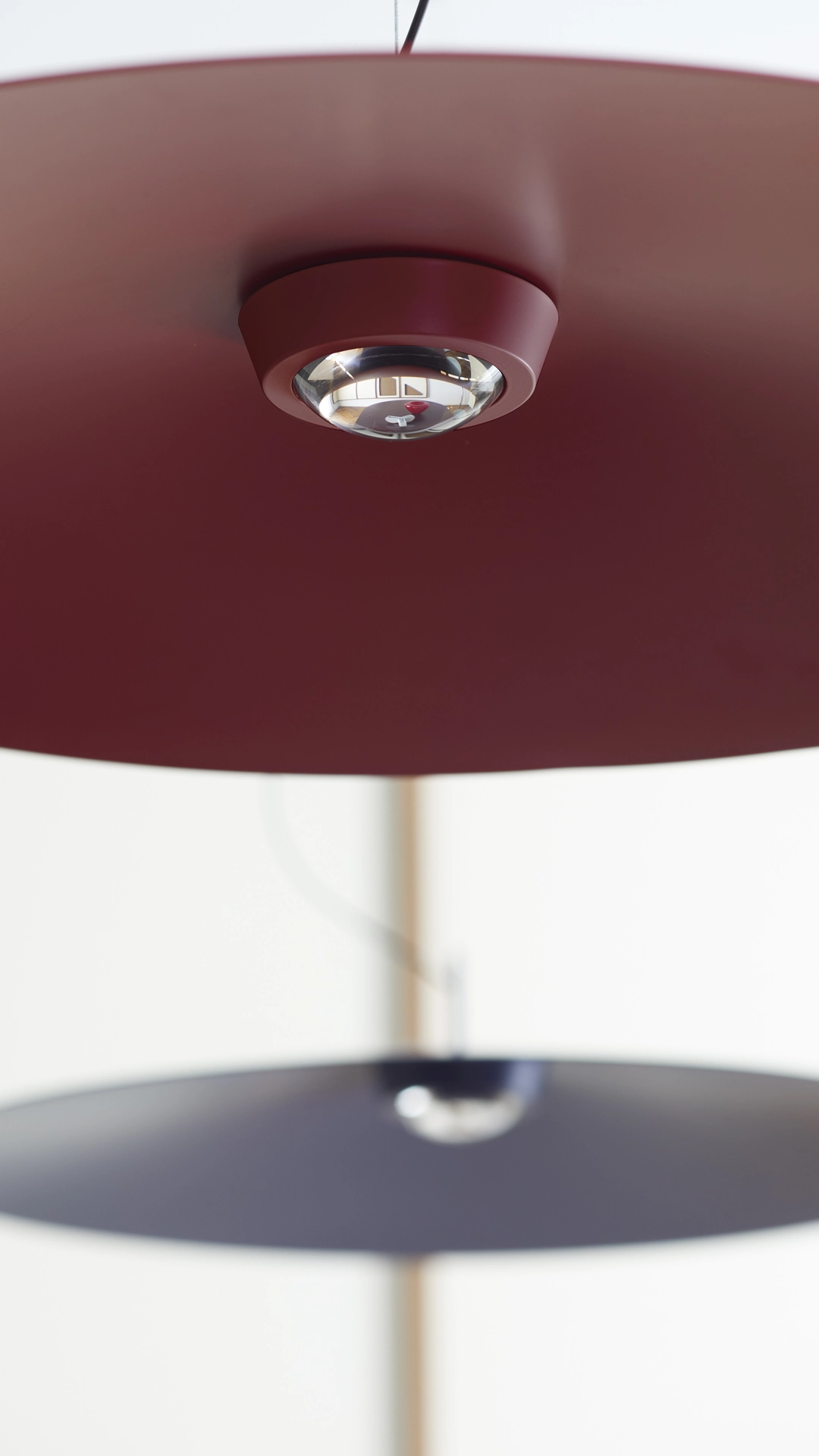
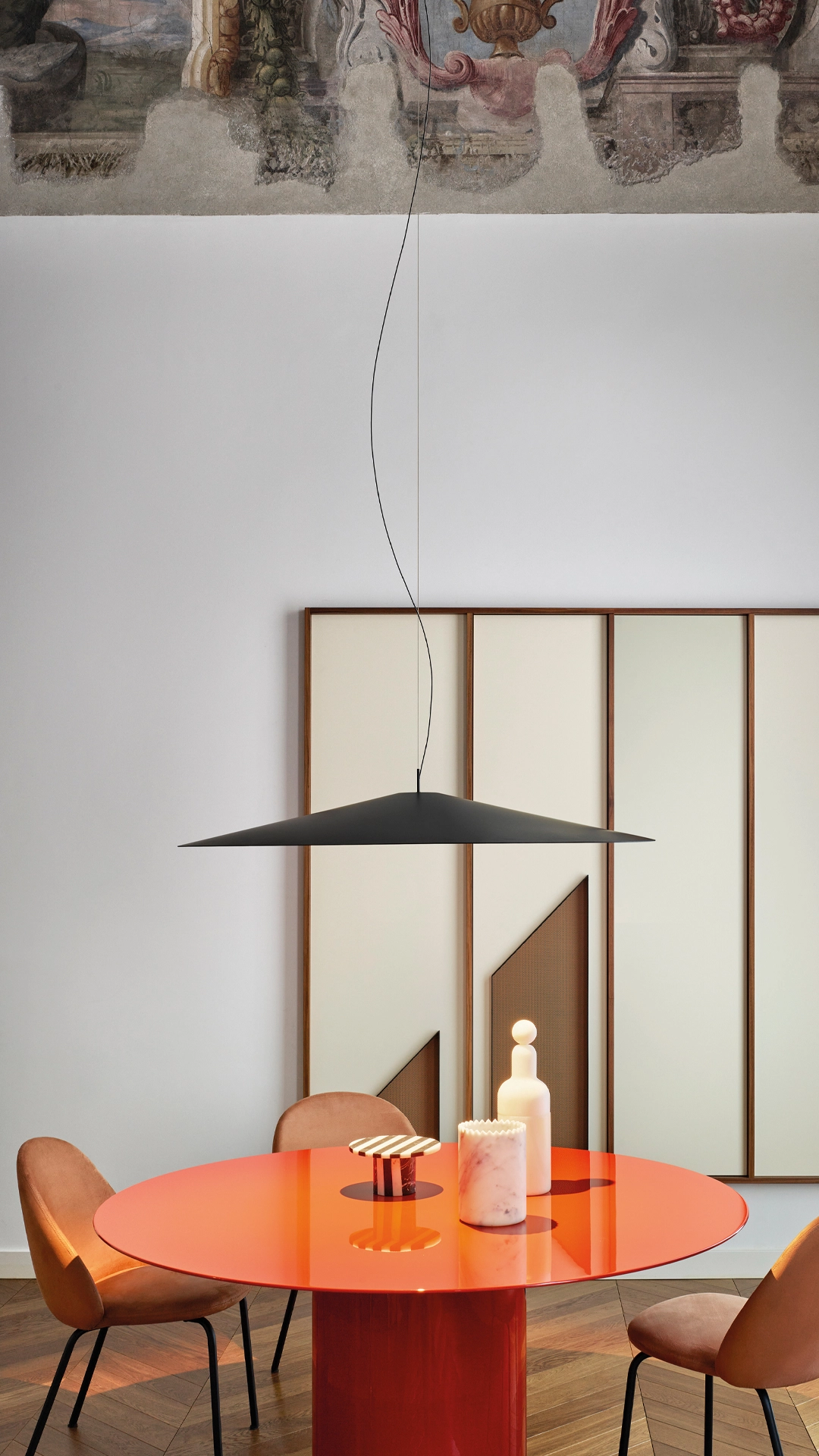
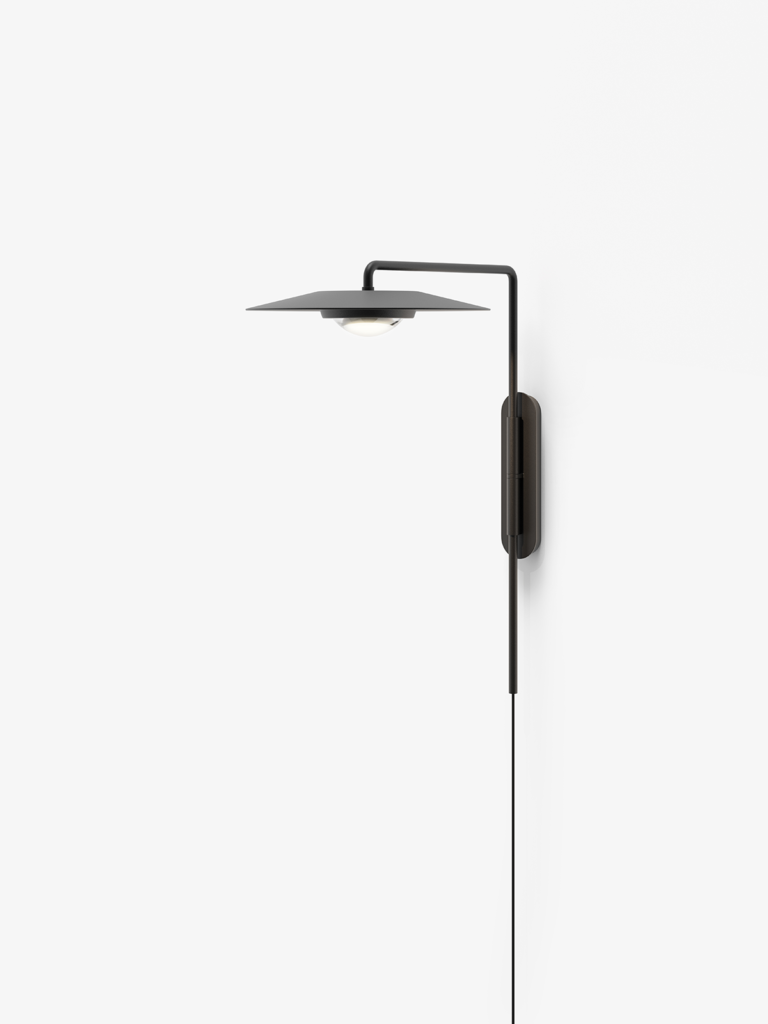
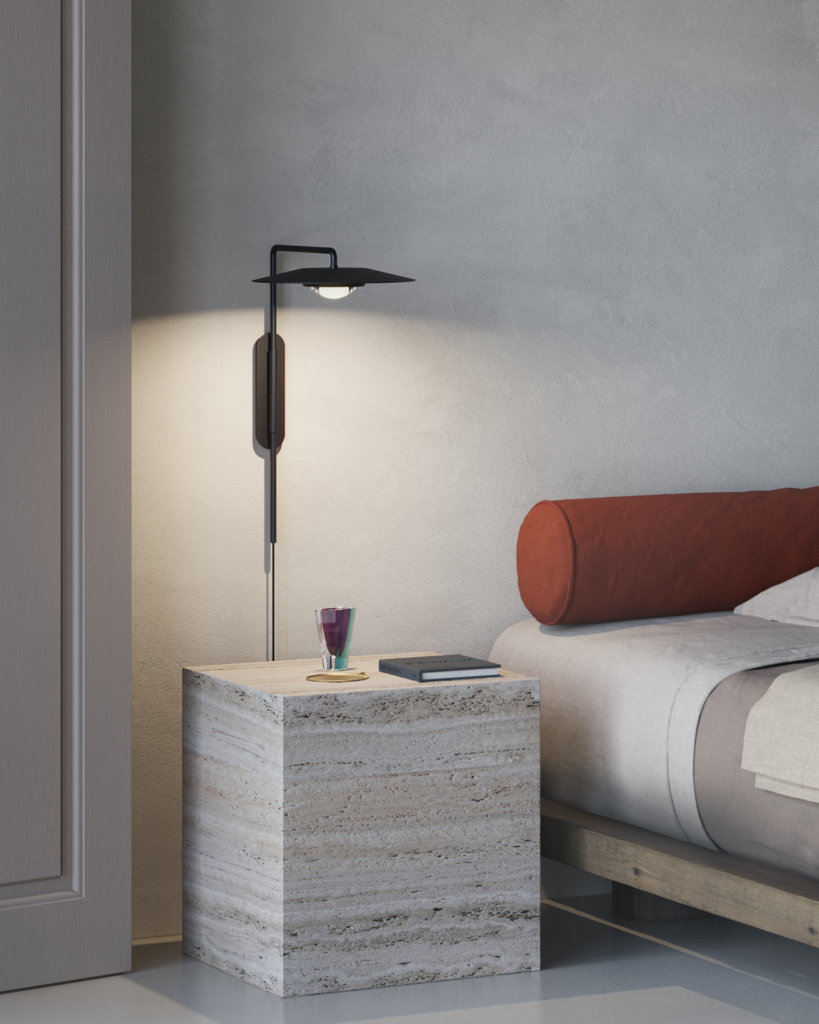
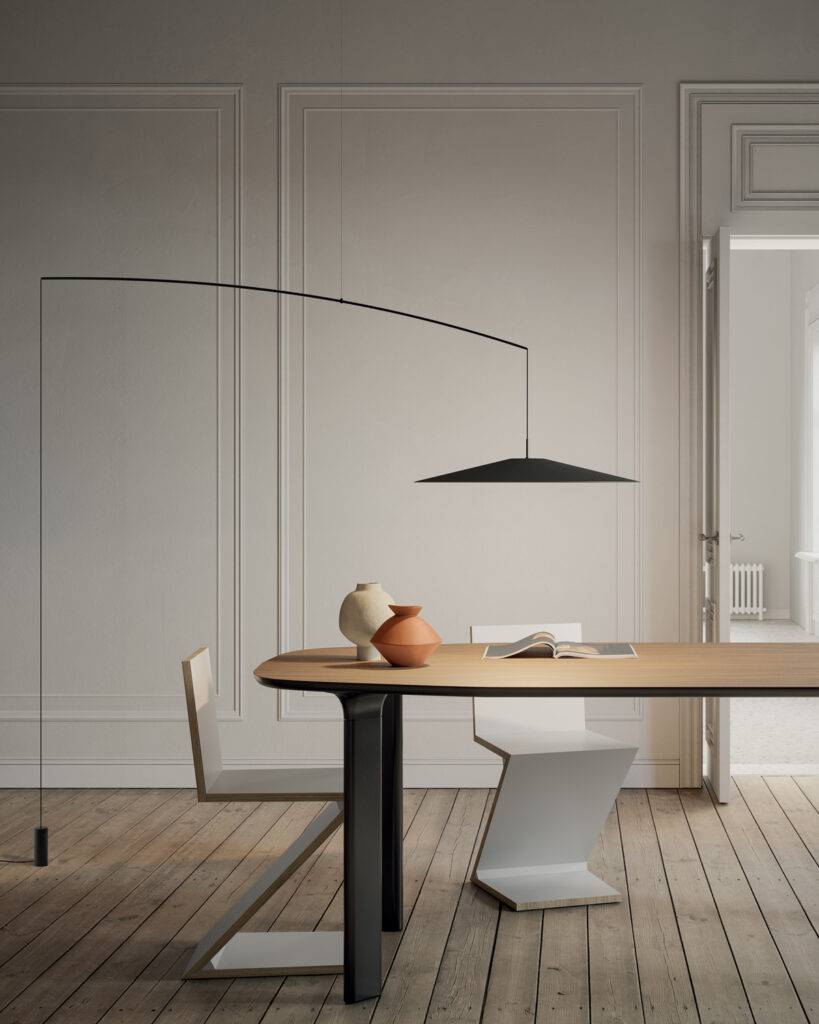
Elegance and purity in form characterise the “Koinè” family of pendant lights, named for its meaning of “shared language” and for its shapes which make it extremely versatile. The light source features a specially designed mineral lens. The light beam distributed by the lens is homogenous and distinct, a broad cone of light with clearly-defined edges
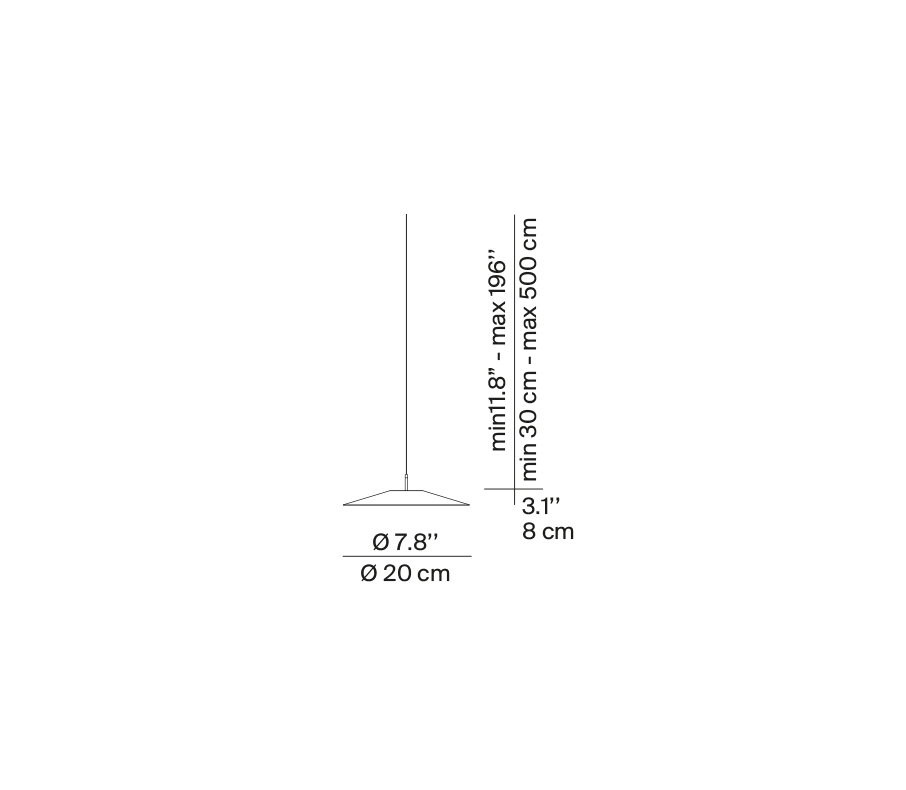
A07S20W A07S20
Koinè Ø 20
A07S20W A07S20
Koinè Ø 20
Main specifications
| Typology | Suspension | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Application | Indoor | ||||||
| Material |
|
||||||
| Finishes |
|
||||||
| Dimensions (mm) | H body 70, cable max 5000, D ø 200 | ||||||
| Weight (kg) | 0.45 | ||||||
| Light Source | LED 12W (only light source – for more details, download datasheet), 2700K, 3000K, CRI 90 | ||||||
| Insulation Class | III |
A07S37WN A07S37N
Koinè Ø 37

A07S37WN A07S37N
Koinè Ø 37
Main specifications
| Typology | Suspension | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Application | Indoor | ||||
| Material |
|
||||
| Finishes |
|
||||
| Dimensions (mm) | H body 80, cable max 5000, D ø 370 | ||||
| Weight (kg) | 1.1 | ||||
| Light Source | LED 19W (only light source – for more details, download datasheet), 2700K, 3000K, CRI 90 | ||||
| Insulation Class | III |
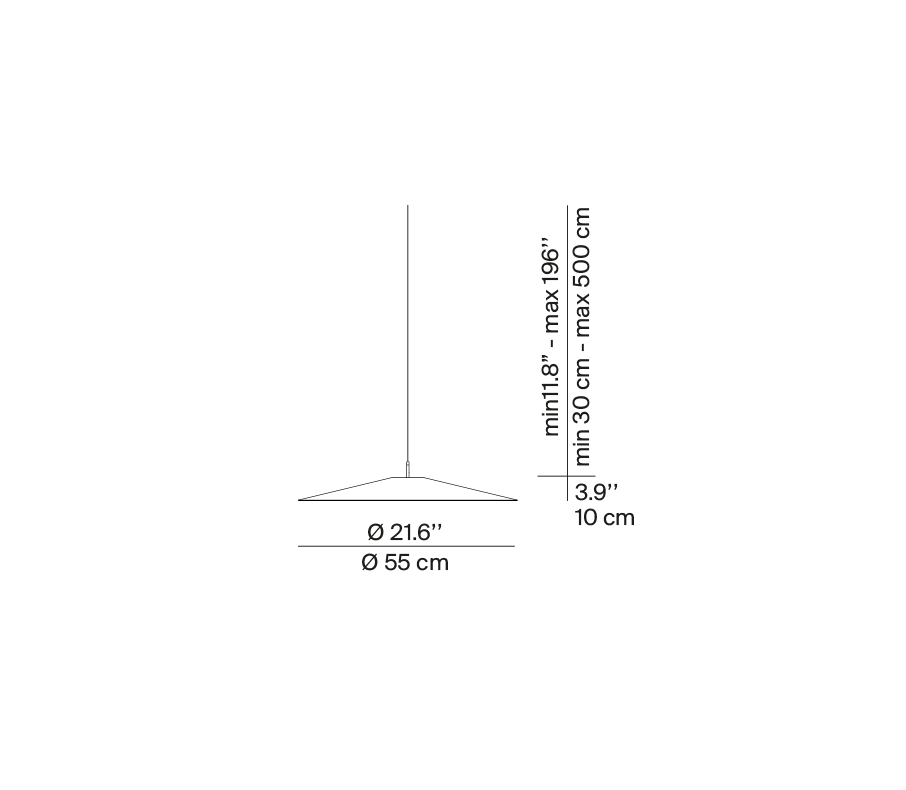
A07S55WN A07S55N
Koinè Ø 55
A07S55WN A07S55N
Koinè Ø 55
Main specifications
| Typology | Suspension | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Application | Indoor | ||||
| Material |
|
||||
| Finishes |
|
||||
| Dimensions (mm) | H body 100, cable max 5000, D ø 550 | ||||
| Weight (kg) | 1.5 | ||||
| Light Source | LED 19W (only light source – for more details, download datasheet), 2700K, 3000K, CRI 90 | ||||
| Insulation Class | III |
A07S86W A07S86
Koinè Ø 86
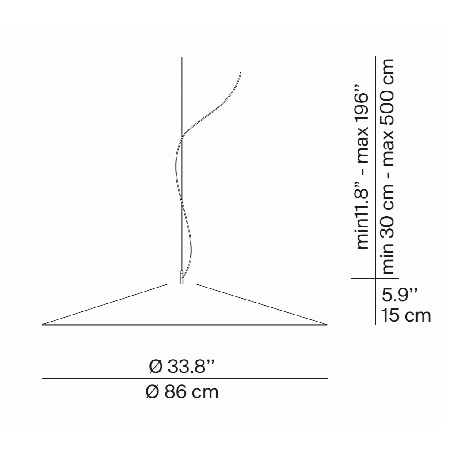
A07S86W A07S86
Koinè Ø 86
Main specifications
| Typology | Suspension | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Application | Indoor | ||
| Material |
|
||
| Finishes |
|
||
| Dimensions (mm) | H body 150, cable max 5000, D ø 860 | ||
| Weight (kg) | 3 | ||
| Light Source | LED 26W (only light source – for more details, download datasheet), 3000K, CRI 90 | ||
| Insulation Class | III |
A07S11N A07S11WN
Koinè Ø 110

A07S11N A07S11WN
Koinè Ø 110
Main specifications
| Typology | Suspension | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Application | Indoor | ||||
| Material |
|
||||
| Finishes |
|
||||
| Dimensions (mm) | H body 150, cable max 5000, D ø 1100 | ||||
| Weight (kg) | 6 | ||||
| Light Source | LED 26W (only light source – for more details, download datasheet), 3000K, 2700K, CRI 90 | ||||
| Insulation Class | III |
Insights