Designers
Mandalaki Studio


1/2
2/2
Mandalaki è uno studio di design di prodotto e consulenza fondato nel 2012 da Enrico De Lotto, George Kolliopoulos e Giovanni Senin a Milano, Italia. Davide Giovannardi è diventato socio nel 2013. Il team ha una formazione diversa in Product Design, Economia e Arte.
Mandalaki esplora l’intersezione tra design e tecnologia per creare pezzi unici di alta qualità e valori concettuali come risultato del loro approccio innovativo e coerente tra processi industriali e artigianali. Forme estremamente pure nascondono anni di meticolosa ricerca tecnica ed estetica che caratterizzano i loro prodotti, architetture e opere d’arte iconiche e riconoscibili.
Ogni progetto è collegato l’uno all’altro: dalle microcase modulari alle auto elettriche, dalle installazioni luminose ai mobili. I progetti sono guidati dalla ricerca di essenzialità e funzionalità, oltre che di sostenibilità e performance.
Prodotti correlati

Koinè Sospensione,
Designed by Mandalaki Studio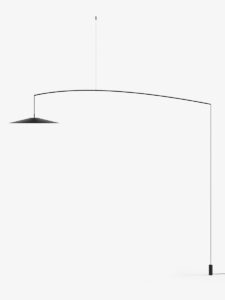
Koinè Terra,
Designed by Mandalaki Studio
Koinè cluster Sospensione,
Designed by Mandalaki Studio
Koinè Sistema binario,
Designed by Mandalaki Studio